Emerging materials 2020
About Conference
Emerging Materials Conference team grandly welcome all the participants from all over the world to attend the “20th International Conference on Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology. Emerging Materials 2020 includes prompt keynote presentations, oral talks, poster presentations , scientific sessions, plenary lectures, world class Exhibitions, diverse Symposiums, highly enriched workshops and B2B meetings related to Material Science, Emerging Materials, Nanotechnology, Nanoengineering, Nanomaterials, Materials Structures, Mechanical, Computers, Electrical & Electronics, Material, Biomaterial, Materials Chemistry, Medical Sciences & Related Departments. All Academia and Business Companies find the fantastic opportunity to collaborate and access the New Technologies, sharing the knowledge across the globe.
Importance and Scope:
Emerging Materials are the group of materials which are also called as functional materials. The energy forms that get featured in materials are thermal energy, electric energy, magnetic energy, sound energy & mechanical energy. Emerging Materials or smart structures are those which join the category of actuators and sensors that highly incorporate into the structures and have basic functionality and in addition extremely integrated control logic, signal power amplification electronics and signal conditioning. The Emerging Materials is anticipated to be the significant world-shattering force that results in influencing the human life and economy. It is strongly understood that mutual impact of industrial and information technology may approach the magnitude of change that could result from commercialization of Emerging Materials.
Why to attend:
Emerging Materials with its running theme aims in accelerating the research and in promoting the knowledge across the globe. Emerging Materials 2020 conference is the best podium to exchange ideas and to make new contacts with new people and organizations internationally. It is an eccentric occasion to collaborate with numerous people through collaboration spaces and break-out rooms. It allows delegates and the speakers to access the new technology and to get aware of the current trends in the field of Material science, Emerging Materials, Mechanical, Automobile, Aviation, Nanotechnology, Electronics, Electrical, Biotechnology, Medical, Defence related fields.
Target Audience:
Material Science, Emerging Materials, Computers, Electrical & Electronics, Physical Sciences, Nanoscience &Nanomaterials, Nanotechnology, Biomaterials, Materials Chemistry, Mechanical, Architecture & Civil, Medical Sciences & related Departments, societies & associations
- Eminent Scientists
- Research Professors & Research fellows
- Directors & Materials Engineers
- Students
- Members of different Emerging Materials Associations & Societies
- Engineering Professors & Faculty
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Medical Devices Software Developer Companies
Sessions/Tracks
Track 1: Emerging Materials and Technology
As the universal require for energy is expected to continue to enlarge at a rapid rate, it is critical that enhanced technologies for sustainably producing, converting and storing energy are developed. Materials are key roadblocks to improved performance in a number of important energy technologies including energy storage in batteries and super-capacitors and energy conversion through solar cells, fuel cells, and thermoelectric devices.
- Sensors based on emerging devices
- Advanced Materials for energy
- Thermoelectric materials
- Transparent Conductors
- Memory Devices
- Chemical Sensors
- Smart materials
- Light-weight energy-efficient structural materials
- Solar energy conversion
- Materials and structures for energy conservation and solar devices
- Emerging areas of Materials Science
Track 2: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is well-defined as the handling of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale. Earlier, Nanotechnology was defined as the area of employing atoms and molecules to produce nanoscale products, which are also referred to as molecular nanotechnology. The National Nanotechnology initiative, has defined nanotechnology as the management of material with the measurement of 1 to 100 nm. Nanomaterials are physical materials with a characteristic measurement between 1-150nm that are the building blocks of applied nanotechnology.
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nanotechnology for Energy and the Environment
- Risks and Regulation of Nanotechnology
- Nanocharacterization & Nanomanufacturing
- Medical and Science Nanotechnology
- Nanosafety
- Nanodiamond devices
- Nanomedicine
- Nanomedicine and Biomedical Engineering
Track 3: Materials Science and Engineering
Materials Science and Engineering can subdiscipline as Materials Science and Materials Engineering. “Materials science” investigates the relationships that exist between the structures and properties of materials. In contrast, “materials engineering” is, on the basis of these structure–property correlations, designing or engineering the structure of a material to produce a predetermined set of properties. It is the design and discovery of new materials, particularly solids. Virtually all important properties of solid materials may be grouped into six different categories: mechanical, electrical, thermal, magnetic, optical, and deteriorative. For each there is a characteristic type of stimulus capable of provoking different responses. Mechanical properties relate deformation to an applied load or force; examples include elastic modulus and strength.
- Materials Synthesis
- Quantum Materials
- Novel Materials, Multifunctional Materials
- Transistor gate materials
- Photovoltaics
- Magnetic Materials
- Fracture analysis
- Materials in the field of Medicine
- Materials Characterization
- Materials – Computational Methods
- Materials Processing
- Materials Innovation and Development
Track 4: Materials for Regenerative Medicine, Drug delivery and Cosmetics
The field of regenerative medicine has tremendous potential for improved treatment outcomes and has been stimulated by advances made in bioengineering over the last few decades. The strategies of engineering tissues and assembling functional constructs that are capable of restoring, retaining, and revitalizing lost tissues and organs have impacted the whole spectrum of medicine and health care. Techniques to combine biomimetic materials, cells, and bioactive molecules play a decisive role in promoting the regeneration of damaged tissues or as therapeutic systems.
- Hydrogels Implementation
- Materials in medicine
- Cosmetic Materials
- Materials for Drug Delivery
- Materials Biology
Track 5: Soft Materials and Polymers
Soft matter or soft condensed matter is a subfield of condensed matter comprising a variety of physical systems that are deformed or structurally altered by thermal or mechanical stress of the magnitude of thermal fluctuations. They include liquids, colloids, polymers, foams, gels, granular materials, liquid crystals, pillows, flesh, and a number of biological materials.
- Colloids
- Complex fluids
- Fracture of soft materials
- Granular materials
- Automobile
- Biomedical Applications
- Civil Engineering of Mega Structures
- Aerospace Applications
- Microstents
- Microsurgery
- Textile
- Damping Elements
- Structural Materials
Track 6: Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering
Biomaterial is defined as a substance that has been engineered to interact with components of living system for both therapeutic and diagnostic purpose. Biomaterials are natural components or it can be synthesized in the laboratory employing metals, ceramics, polymers and composite materials. Biomaterials covers the fundamentals of medicine, biology, chemistry, tissue engineering and materials science. The biomaterial science also includes polymer synthesis, drug design, self-assembly of materials, immunology and toxicology. Biomaterials has its wide usage in drug delivery, dental application, surgery and regenerative medicine that mimics the natural function.
- Nanoelectronics and Quantum nanodevices
- Nanomedicine and Bionanotechnology
- Bio-fuels and Bio-energy
- Tissue Engineering/Regenerative Medicine
- Single Cell Analysis
- Cell Manufacturing
- Shape-memory alloys for biomedical implants
- Biocompatible polymers for tissue engineering
- Self-Assembly Biointerfaces and Biodevices
- Fusion of NanoBio and Information Science
- Biomembranes
Track 7: Materials Physics and Chemistry
Materials Chemistry provides the loop between atomic, molecular and supermolecular behaviour and the useful properties of a material. It lies at the core of numerous chemical-using industries. This deals with the atomic nuclei of the materials, and how they are arranged to provide molecules, crystals, etc. Much of properties of electrical, magnetic particles and chemical materials evolve from this level of structure. The length scales involved are in angstroms. The way in which the atoms and molecules are bonded and organized is fundamental to studying the properties and behaviour of any material.
Material physics is the use of physics to describe the physical properties of materials. It is a synthesis of physical sciences such as chemistry, solid mechanics, solid state physics, and materials science. Materials physics is considered a subset of condensed matter physics and applies fundamental condensed matter concepts to complex multiphase media, including materials of technological interest.
Track 8: Electrical, Optical, Magnetic Materials
Materials which can be magnetized and attracted to a magnet are termed as ferromagnetic materials. These kind of ferromagnetic materials comprise of iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Magnetic Smart Materials also have medical applications and it is predictable that they will increase in the future. Examples are carrying medications to exact locations within the body and the use as a contrasting agent for MRI scans, evaluating the risk of organ damage in hereditary hemochromatosis, defining the dose of iron chelator drugs mandatory for patients with thalassemia, and Now-a-days Scientists are also occupied on the advancement of synthetic magnetic particles which can be inoculated into the human body for the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Spintronic, also known as spin electronics or fluxtronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its related magnetic moment, in addition to its vital electronic charge, in solid-state devices.
- Quantum Dots
- Electrical Steels
- Optical Characteraization
- Magneto-Optical and Photo magnetic effects
- Meta materials
Track 9: Advancement of Graphene Physics and 2D Materials
Graphene is the crystalline form of carbon that has two dimensional (2D) properties where it consists of single layer of carbon atom arranged in hexagonal lattice. This allotrope of carbon is the basic structure of other allotropes such as diamond, carbon nanotubes, graphite, fullerenes. Graphite which is one of the allotrope of carbon is the softest material with is very good lubricant and is the conductor of electricity. Because of its known unique property, it is being used as thermal insulation. Natural graphite is of three types as crystalline, amorphous and vein. Carbon has numerous essential application in the living system. Carbon fibers which is composed mostly of carbon events, in the range of 5-10 micrometers has its application in composite materials, textiles, microelectrodes, Flexible heating. Carbon Nanotube is the cylindrical form of the allotropes of carbon has unusual thermal conductivity, mechanical and electrical properties and is valuable in the arenas of materials science, nanotechnology, electronic and optics.
- Carbon nanotubes
- Graphene and fullerenes
- Graphene and ultra tin 2D materials
- Graphene 3D printing
- Uses on carbon Nanotubes
- Graphene The Ultra-Capacitor
- Graphene devices
- Acutators
Track 10: Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
The field of pharmaceutical nanotechnology provides an insights into the study of synthesis, characterisation and diagnostic application of materials at the nanoscale. The particular interest within the field is synthesis, characterisation, biological evaluation, clinical testing and toxicological assessment of nanomaterials as drugs for various diseases.Nanotechnology is the science which deals with the processes that occur at molecular level and of nanolength scale size.
The major studies in the nanotechnology include nanosized particles, their function and behaviour with respect to other systems. The tremendous capabilities of nanoparticles have changed the perspective and scope of nanotechnology towards development into an adjuvant field for the remaining fields of life sciences.
- Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
- Drug Targeting
- Drug Delivery Research
- Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Challenges and advances in Nano Pharmaceuticals
- NanoPharmaceuticals from the bench to Scale up
- Future aspects of Nano Pharmaceuticals
Track 11: Polymer Science and Technology
Polymer technology is one of the most prevalent zone of existing research as it includes the study and application of nanoscience to polymer-nanoparticle matrices, where nanoparticles are those with at least in dimension of less than 100 nm. Polymer nanotechnology emphases on polymer based biomaterials, self- assembled polymeric films, nanofabrication of polymers, polymer blends and nanocomposites. Polymer matrix based nanocomposites consist of polymer or copolymer having nanoparticles dispersed in the matrix. Silicon Nano spheres is the extensively known Nano polymer which shows discrete features and harder than silicon. Preceding the age of nanotechnology phase, polymer blends, block copolymer domain frequently attains Nano scale sizes. Nano-sized silica particles, zeolites and nanoparticle fillers has controlled the expansion of products with enhanced properties such as thermal stability & conductivity, chemical resistance and tensile strength.. Some of the natural and synthetic polymers are collagen, enzymes, elastin, cellulose, chitin, plastics, fibers and adhesives.
- Polymer electronics and photonics
- Aqueous Coatings
- Biodegradable Waxes
- Renewable Hot Melt Adhesives
- Biodegradable Polymers
- Nanotechnology in Polymers
- Nanomaterial-polymer composite materials with superior mechanical properties
- Polymer-nanomaterial composites
- Conducting polymers
- Antifouling polymers
- 3D print manufacturing
Track 12: Nano Robotics
Nanorobotics is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometre (10−9 meters). More specifically, nanorobotics (as opposed to microrobotics) refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots. Nanomachines are largely in the research and development phase.
- Nano Biometric
- Molecular Mimics
- Lipids As Nano - Bricks And Mortar
- self-organizing supra molecular structures
- Biological Computing- A Protein- Based 3d Optical Memory Based On Bacteriorhodopsin
Track 13: Smart Materials
Smart materials can be defined as materials that can significantly change their mechanical properties (such as shape, stiffness, and viscosity), or their thermal, optical, or electromagnetic properties, in a predictable or controllable manner in response to their environment. Such materials have the ability to change shape or size simply by adding a little bit of heat, or to change from a liquid to solid almost instantly. Each individual type of smart material has a different property such as volume, viscosity, and conductivity which can be significantly altered.
- Nanoplasmonic structures
- Super hard Materials
- Intelligent sensors
- Nanomaterials in Human Experience
- Amorphous Materials
- Thermodynamics of materials
- Single-molecule electronics
- Single-molecule electronics
- Transparent conducting thin films
- Future of 3D Printing
Track 14: Nanotechnology in Water Treatment
Nanotechnology refers to a broad range of tools, techniques and applications that simply involve particles on the approximate size scale of a few to hundreds of nanometers in diameter. Particles of this size have some unique physicochemical and surface properties that lend themselves to novel uses. Indeed, advocates of nanotechnology suggest that this area of research could contribute to solutions for some of the major problems we face on the global scale such as ensuring a supply of safe drinking water for a growing population, as well as addressing issues in medicine, energy, and agriculture.
- Nanomaterials and water filtration
- Bioactive nanoparticles for water disinfections
- Self-assembled monolayer on mesoporous supports (SAMMS)
- Bimetallic iron nanoparticles
- Nanoscale semiconductor photocatalysts
Track 15: Advanced Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials are characterized as materials of which a solitary unit is measured 1 and 1000 nanometers yet is generally 1—100 nm. Materials with structure at the Nano scale regularly have one of kind optical, electronic or mechanical properties. Nanomaterial’s enquires about adopting the approaches related to materials science and nanotechnology.
- Novel Magnetic-Carbon Biocomposites
- Gold Nanoparticles and Biosensors
- Recent Studies of Spin Dynamics in Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles
- ZnO Nanostructures for Optoelectronic Applications
- Thin Film and Nanostructured Multiferroic Materials
Track 16: Nano Fluidics
Nanofluidics is the study of the behavior, manipulation, and control of fluids that are confined to structures of nanometer (typically 1–100 nm) characteristic dimensions (1 nm = 10−9 m). Fluids confined in these structures exhibit physical behaviors not observed in larger structures, such as those of micrometer dimensions and above, because the characteristic physical scaling lengths of the fluid, (e.g. Debye length, hydrodynamic radius) very closely coincide with the dimensions of the nanostructure itself.
All electrified interfaces induce an organized charge distribution near the surface known as the electrical double layer. In pores of nanometer dimensions the electrical double layer may completely span the width of the nanopore, resulting in dramatic changes in the composition of the fluid and the related properties of fluid motion in the structure
- Nanofluidic structures
- Tuneable Microlens Array
- Nanofluidic circuitry
- Microfluidic cell sorting and Analysis
- Nanofluidic Devices for DNA Analysis
- Nano Pathology
Track 17: Nano Photonics
Nanophotonics or nano-optics is the study of the behavior of light on the nanometer scale, and of the interaction of nanometer-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology. It often (but not exclusively) involves metallic components, which can transport and focus light via surface plasmon polaritons.Nano photonics is where photonics merges with Nano science and nanotechnology, and where spatial confinement considerably modifies light propagation and light-matter interaction
- General Introduction
- Review of Fundamentals of Lasers
- Description of Light as an Electromagnetic Wave
- Definition of Photon
- Scanning Electron Microscope
- Nanodots
Track 18: Insight on Emerging Materials
Emerging material can be defined as material that can significantly change their mechanical properties (such as shape, stiffness, and viscosity), or their thermal, optical, or electromagnetic properties, in a predictable or controllable manner in response to their environment. Such materials have the ability to change shape or size simply by adding a little bit of heat, or to change from a liquid to solid almost instantly. Each individual type of emerging material has a different property such as volume, viscosity, and conductivity which can be significantly altered.
- Composite Materials
- Materials Theory
- ElectroChemical Materials
- Complex Materials
- Multifunctional Ferroic Materials
- Natural & Synthetic Materials
- High Temperature Materials
- Photovoltaic
- pH Sensitive
- Halochromic
- Dielectric Elastomers
- Integrated system design and implementation
- Piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials
- Shape-memory alloys
- Electroluminescent materials
- Polymer-based smart materials
Market Analysis
SUMMARY:
(Theme: Unveiling the Innovations in Material Science and Nanotechnology for better future)
The “20th International Conference on Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology” is the podium to share and gain knowledge from the novel technological developments in the field of science, Engineering and Technology. This conference brings together professors, researchers, scientists, students in all the areas of Material science, Engineering and Nanotechnology. It offers an international opportunity for the spreading of approved research. We are honoured to invite you all to attend and register for the 20th International Conference on Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology. Emerging Materials 2020 is scheduled for November 23-24, 2020 in Budapest, Hungary.
The organizing committee is spacing out for an exciting and enlightening conference program that comprises of plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on multiple topics, poster presentations and numerous programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at 20th International Conference on Emerging Materials and Nanotechnology, where you will be sure of having an eloquent experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Emerging Materials 2020 organizing committee look forward to meeting you in Budapest, Hungary.
Importance & scope:
The Material Research encompasses the fundamental studies of materials structure - property relationships for the current and future importance in the field of science and engineering. The development of materials in industrial application was improved by the formation of academic programs and research institutes around the globe.
The National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) was established principally since Nano science and technology are foretold to have a huge potential economic impact. It is strongly believed that mutual impact of industrial and information technology may approach the magnitude of change that could result from commercialization of material nanotechnology.
The emphasis on the processing of new materials facilitates its applications to the next generation of engineers and its high marketability has a great impact on the economy. In the new decade, the sustainability and influence on the environment lie in the core of the material improvement.
Why to attend?
Emerging Materials 2020 provides a striking opportunity to meet and make new contacts that link us with delegates who are active in the field of material science, Biomaterials and nanotechnology. It offers comprehensive sessions on recent strategies and advances in the development of new materials. Networking enables sharpening skills, spark inspiration and uncover new ideas during break-out sessions providing tea and lunch for the delegates. The important subjects are addressed by the expertise key note speakers with global recognition thus conferring knowledge on the new technologies and latest drift in the domain. The 19th International Conference on Emerging Materials and Structures accents the prominent key note speakers, plenary speeches, young research forum, poster presentations, technical workshops and career guidance sessions.
Global Markets of Materials:
The universal Emerging Materials market is expected to spread USD 98.2 billion by 2025, affording to a report by Grand View Research, Inc. Extensive research & innovation activities have expanded the industrial applications of emerging materials. Enlarged usage of smart actuators & motors, sensors, and structural materials is predicted to boost the demand over the next few years.
Emerging materials are innovative products that can sense and respond to a wide-ranging stimuli, comprising electric and magnetic fields, mechanical stress, hydrostatic pressure, nuclear radiation, temperature, pressure, and pH change. Exclusive properties of these products allow them to revert to their original state after removal of the stimuli.
Piezoelectric, electrostrictive, electrochromic, magnetostrictive, phase change, shape memory materials have engorged extensive industrial acceptance in the current past. Moreover, ferromagnetic electroactive polymers, conductive polymers, carbon nanotube actuators and shape memory alloys, are few of the budding materials in the market, with vigorous application.
North America was the foremost area in the worldwide market in 2016, mainly due to significant claim for smart actuators & motors in crucial industries such as automotive, aerospace and consumer goods. Europe has been the second-largest share of the market in 2016, trailed by Asia Pacific. Asia Pacific is projected to unveil a extraordinary development over the prediction period, due to noteworthy research activities reinforced by the government.
The metamaterial marketplace is likely to be valued at USD 4,634.8 Million by 2025, at a CAGR of 63.1% from 2017 to 2025. The cumulative apprehension for variability in design functionalities, anti-glare coating applications, and invisibility cloak for stealth aircraft are the significant aspects to drive the development of metamaterial market.
The Emerging materials & technologies in electronics signify the novel or modification to the current materials & technologies to attain superior performance or efficiency. The market for the topmost advanced materials & technologies in electronics is observing high growth due to the rising end-use applications, technological advances, and the high demand of these technologies from both the industrialized and developing regions.
The LED materials market is expected to reach USD 12.55 Billion by 2021, at a CAGR of 9.9% between 2016 and 2021. The rising demand of LEDs in general and automotive lighting drives the LED materials market. The base year for the study is 2015, whereas the predictable retro is from 2016 to 2021.
The worldwide core materials market for composites is predictable to rise from USD 1.17 Billion in 2016 to USD 1.92 Billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 8.77% from 2017 to 2022. The usage of core materials is becoming dynamic in wind energy, aerospace, marine, transportation, construction and other industries. The leading manufacturers of core materials are Evonik Industries AG (Germany), Armacell International S.A (Luxembourg), Plascore Incorporated (U.S.), Euro-Composites S.A (Luxembourg), Diab Group (Sweden), 3A Composites (Switzerland), Gurit Holding AG (Switzerland), Hexcel Corporation (U.S), and The Gill Corporation (U.S.). These producers executed numerous organic and inorganic developmental methods.
The global aerospace materials market is likely to reach USD 25.80 Billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 6.9% between 2017 and 2022. Increased passenger transportation is expected to develop the aircraft production industry that initiates the demand for aerospace materials. The primary aerospace material companies are Alcoa Corporation (U.S.), Cytec Solvay Group (Belgium), Constellium N.V. (Netherlands), Du Pont (U.S.), Teijin Limited (Japan), ATI Metals (U.S.), Toray Industries, Inc. (Japan)
The locomotive lightweight material market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 13.06% between 2016 and 2021 and achieve a market size of USD 110.42 Billion by 2021. The significant drivers of the market are the rigorous emission and fuel economy regulations, coupled with the targets on weight reduction, by the regulatory authorities and the rise in sales of electric vehicles in the emerging countries.
The silicon carbide (SiC) market size is likely to be esteemed at USD 617.4 Million by 2022, at a CAGR of 17.4% from 2017 to 2022. The features such as the capacity of SiC devices in semiconductor to perform at high temperature and high voltage and power, growing demand for motor devices, ability to decrease the overall system size, and rising applications of SiC in radio frequency (RF) devices and cellular base station are projected to drive the progress of silicon carbide market
The soft magnetic materials market is expected to achieve USD 42.14 Billion globally in 2026, at a CAGR of 8.1%, between 2016 and 2026. Soft magnetic materials offer good permeability and help in the decrease of eddy current losses. Companies are capitalizing in R&D for the growth and building of high quality soft magnetic materials. The cumulative automotive end-user industry is one of the chief drivers for the soft magnetic materials market. The soft magnetic materials are tremendously useful in several applications such as motors, transformers, and alternators.
The global 3D printing materials market is predictable to raise from USD 530.1 Million in 2016 to USD 1,409.5 Million by 2021, at a CAGR of 21.60% throughout the same period. The high progress of the market is owing to the adoption of 3D printing technology in Germany, U.S., and developing countries. The rising aerospace & defense, medical & dental, and automotive industries in these countries are driving the 3D printing materials market.
The electric vehicle plastics market is likely to raise at a CAGR of 27.82% from 2016 to 2021, to reach a market size of USD 1.49 Billion by 2021. Main drivers of this market include the favorable government policies, that leads to the advancement in the sales of electric vehicles, stringent emission regulations, demand for light weighting to achieve fuel efficiency, and the demand to improve ergonomics.
Major Material Science Associations around the Globe
- American Chemical Society (ACS)
- American Physical Society (APS)
- The Materials Information Society (ASM International)
- The Materials Research Society (MRS)
- Microscopy Society of America (MSA)
- The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society (TMS)
- Sigma Xi: The Scientific Research Society
- International Society for Optical Engineering (SPIE)
- The American Ceramic Society (ACerS)
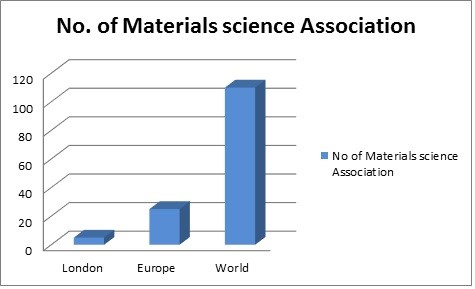
Statistical analysis of Materials Science associations
Major Nanotechnology Associations around the Globe
- EU Seventh Framework Programme (Europe)
- Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory (Brazil)
- National Institute for Nanotechnology (Canada)
- Collaborative Centre for Applied Nanotechnology (Ireland)
- National Nanotechnology Center (Nanotech), Thailand
- Nano medicine Roadmap Initiative (USA)
- American National Standards Institute Nanotechnology Panel (ANSI-NSP)
- Nano Ned (USA)
- National Nanotechnology Initiative (USA)
- National Center for Nano science and Technology (China)
- National Centre for Nano-Structured Materials, CSIR (India)
- Institute of Nano Science and Technology (India)
- Iranian Nanotechnology Laboratory Network (Iran)
- Russian Nanotechnology Corporation (Russia)
- Sri Lanka Institute of Nanotechnology (Sri Lanka)
Target Audience:
- Materials Scientists/Research Professors/ Nanotechnologists
- Physicists/Chemists
- Junior/Senior research fellows of Materials Science/ Nanotechnology
- Materials Science Students
- Directors of material companies
- Material Engineers
- Members of different Materials science associations
- Members of different nanotechnology associations
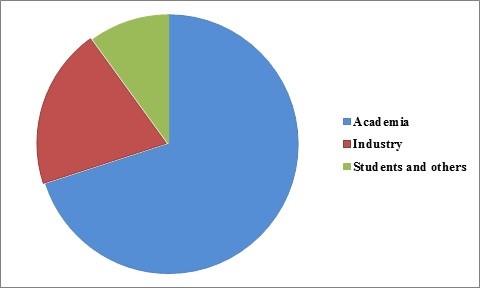
Graphical Representation of Attendance from different sectors:
The global market analysis report in terms of graphical representation
